|
Listen to this Article (Audio)
|
According to Sports AI company Sponsorlytix, there were 622.4 million visits to sports piracy websites and mobile app downloads / activity in 2023. And close to a billion in 2022 due to the FIFA Qatar World Cup 2022. Advertising on illegal streaming sites, mobile apps and fire-sticks subscriptions is estimated to be worth $350 million globally.
The illegal streaming of sports tournaments, leagues and events can cost the industry between $500 million to $1 billion annually in lost sponsorship, advertising and tv broadcast subscription revenues. In 2023, the English Premier League began a crackdown against illegal streams after police raided 1,000 homes, jailed a gang (that sold fire-stick subscriptions), who had earned more than $9 million from subscribers. But as per our research, those numbers do not add up.
Source: Sponsorlytix
But this is just a drop in an ocean with what the sports industry as a whole is up against. The fight against Illegal streamers is a very expensive and exhaustive battle, one that has been on-going for decades. So is there actually a solution? Yes but it is not very simple, it will involve shutting down a whole industry that runs on the internet.
Cryptocurrencies and NFTs experienced a surge during the COVID-19 pandemic, with a notable presence of scams referred to as “alt coins or shitcoins.” Financial transactions occurred globally without a trace, leading to concerns about the government’s inability to regulate blockchain activities. However, it was discovered that cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which rely on mining (requiring storage in GPUs within extensive server rooms), are susceptible to government intervention. Consequently, authorities shut down numerous questionable crypto miners and exchanges, including FTX.
Yet, the challenge remains when it comes to addressing illegal streaming and piracy. It appears that this is the issue that has proven elusive to effective resolution from the authorities.
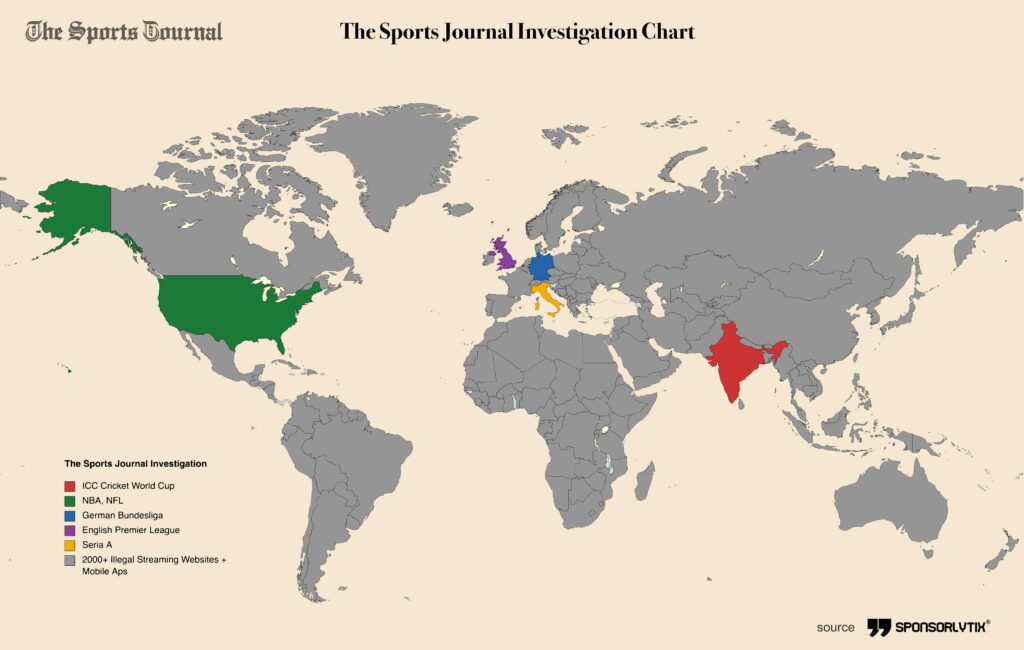
The Sports Journal Investigation
The Sports Journal, in collaboration with Sponsorlytix, undertook a comprehensive analysis of more than 2000 illicit streaming websites and apps. Analysed broadcasters, professional sports leagues from Europe and North America. This extensive study also involved the examination of international sports tournaments and approached governing bodies, such as the National Cyber Security Center in the UK.
the National Cyber Security Center in the UK.
After months of digging through different networks in the dark web, The Sports Journal spoke anonymously in-depth with a streamer to understand the whole process of setting up a stream and the motivations behind their activities, which is “not about the money”, as it was stressed out to us several times.
The Sports Journal then verified the information with a group of talented engineers and looked at the data generated by Sponsorlytix in depth. Kevin Plumb, general counsel for the Premier League, built up an internal team of lawyers, investigators and “content protection analysts” to help remove illegal content and punish those providing it.
![]()
We don’t underestimate them, they’re really sophisticated now. There is always a challenge with finding people online.
Kevin Plumb, General Counsel of the Premier League, speaking to the Financial Times
But lets take a step back and explain, what is Illegal streaming?
Illegal sports streaming refers to the unauthorized rebroadcast of live sports events over the internet. This type of streaming is a violation of copyright laws and can result in legal action being taken against the individuals or organizations involved.
Streamers set up websites or apps that offer live streams of popular sports events without obtaining the necessary permissions from the rights holders. This is done by using various means such as hacking into legitimate streaming services, scraping the web for live streams or setting up their own streaming servers.
Now let us explain how to build and code an illegal streaming broadcast.
Code script verified by professional engineers
In the realm of coding, illicit streaming typically involves the use of harmful code. Streamers employ various techniques like exploiting vulnerabilities, intercepting network data, and cracking credentials. These streamers possess technical skills, enabling them to create a botnet, engage in reverse engineering, and more. Another method involves web scraping, where streamers use code to automatically search the internet for live streams hosted on legitimate websites, such as an official sports league website. Once located, they embed the live stream on their illicit platform, essentially re-broadcasting the content to their audience.
Libraries such as BeautifulSoup, Scrapy or Selenium are some of the ways scraping is used in the process.
Streamers can set up their own streaming servers and use torrents or other peer-to-peer sharing methods to distribute the copyrighted content without permission. This allows them to bypass the need for a website and instead rely on a distributed network of users to share the content.
This involves setting up a streaming server that can handle the streaming protocol, then create a torrent file and seed it to different tracker sites. They might use libraries such as ffmpeg, VLC, and others.
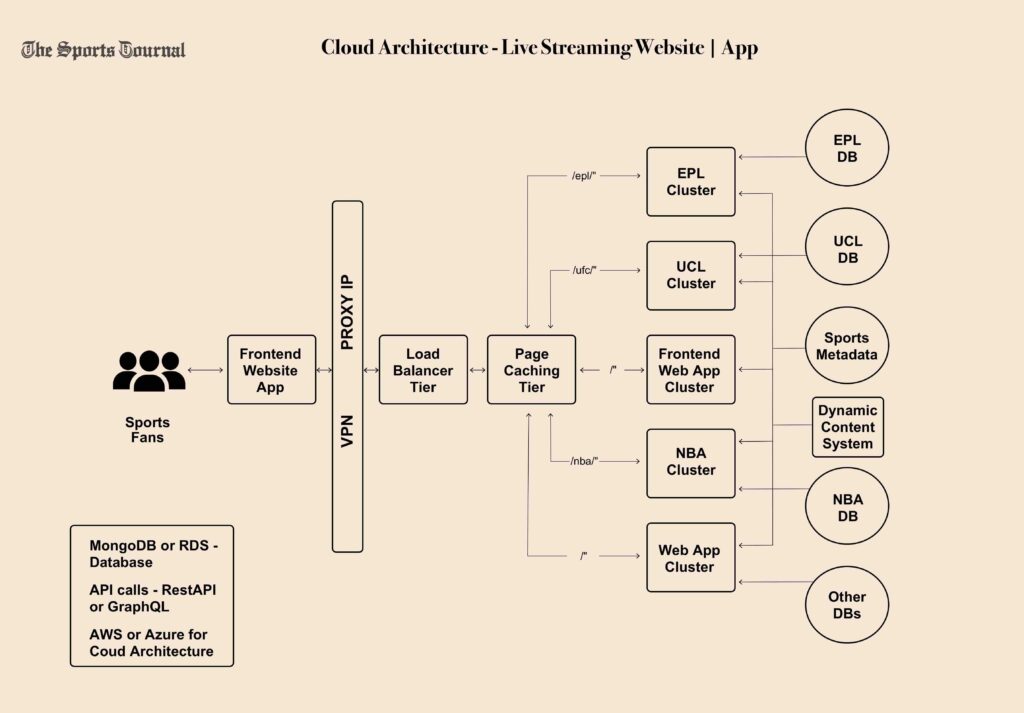
Architecture verified by professional engineers
How do Illegal streamers evade law enforcement authorities?
The world of illegal streaming operates as a complex ecosystem with myriad players and internet nodes, extending beyond comprehensive understanding. It involves a software developer in United States or China, a server farm in Spain or Nigeria, a black-market operator in Bolivia, platforms like Reddit, X (Twitter) and YouTube, obscure top-level domains such as “.sx,” and numerous unseen websites. For example – www.buffstreams.sx
Within this intricate system, the chain of command typically starts with a pirate who employs easily accessible devices to pilfer cable and satellite feeds or employs advanced coding skills and screen-recording programs to extract online streams from official sites like ESPN+ and DAZN.
 The stolen streams undergo further redistribution, often in an automated manner, creating a multi-level sequence of unauthorized activities. Free websites and pirate subscription services become increasingly interconnected, with some re-streamers dedicating significant time to building software that captures a vast majority of the world’s sports TV broadcasts from an online Russian sportsbook.
The stolen streams undergo further redistribution, often in an automated manner, creating a multi-level sequence of unauthorized activities. Free websites and pirate subscription services become increasingly interconnected, with some re-streamers dedicating significant time to building software that captures a vast majority of the world’s sports TV broadcasts from an online Russian sportsbook.
Generally, there are three categories of sites, two of which are visible. One remains unseen as a hosting site, where the pilfered video resides. This stream is then embedded on a destination site, which disclaims legal responsibility for the embedded content. These destination sites often operate in legal gray areas, disguising themselves as blogs or sports news outlets to argue against facilitating unauthorized redistribution as their sole purpose. Example www.totalsportek.com
These destination sites promote themselves on linking sites, which index streams by sport and game, creating legal separation between themselves and the illicit activity. Reddit, with its moderator-verified streamers, serves as a popular linking site, accelerating the growth of the illicit industry.
The main secret sauce that they use are VPNs to mask their location and identity: A virtual private network (VPN) allows a user to create a secure connection to another network over the internet. By using a VPN, illegal sports streamers can hide their IP address and location, making it difficult for authorities to trace the source of the streams.
There are two way to use a VPN: by the way of a code or to use VPN service provider for example NordVPN.
This is a basic VPN code to use while starting your own server and they keep a large list of proxy IPs with them and keep rotating it for extra layer of anonymous security

Code verified by professional engineers
Same goes for the domain, one day they would be using .sx, next day they will switch it to .ag or something else, they just keep on redirecting the blocked site to the new one.
How do illegal streaming Apps evade the iOS & Google App stores approval process?
The app may be submitted under a different name or developer account to avoid detection by the app stores. The app may be designed to hide its illegal streaming functionality, making it appear to be a legitimate app.
The app may be distributed using “side-loading” methods, which allow users to install apps on their devices without going through the official app store. For example, Android phones allows you to install an app on your phone directly by downloading the apk file from the internet, without the need for going through the Google Play Store.
What exact law do they break?
Illegal streaming apps break copyright laws by distributing copyrighted content without permission from the rights holder. This includes streaming movies, TV shows, and live sports events without obtaining the proper licenses or rights to do so.
 In many countries, copyright laws prohibit the unauthorized distribution of copyrighted content, including streaming it over the internet. This means that streaming copyrighted content without permission is illegal, whether it is done for profit or not. Many countries also have specific laws and regulations that target illegal streaming, such as the United States’ Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) and the European Union’s Audiovisual Media Services Directive (AVMSD).
In many countries, copyright laws prohibit the unauthorized distribution of copyrighted content, including streaming it over the internet. This means that streaming copyrighted content without permission is illegal, whether it is done for profit or not. Many countries also have specific laws and regulations that target illegal streaming, such as the United States’ Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) and the European Union’s Audiovisual Media Services Directive (AVMSD).
In the United States, efforts to broaden copyright legislation in order to address live streaming issues have failed. Despite advocacy from major sports leagues, their endeavors have been unsuccessful. A legislative proposal in 2012, referred to as the Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA), aimed to enhance law enforcement’s jurisdiction in the digital realm. However, the idea of restricting internet freedoms encountered robust opposition from influential tech companies, leading to its ultimate demise.
![]()
And what happens to people who steal? You get f***ing smashed and you go to jail that is what happens to you, and I make sure that we get you. Everybody was f***ing laughing when I was talking about this but we caught a lot of people. People weren’t laughing when they got caught, and I had a lot of people begging me not to prosecute them but stealing is stealing.
We’ve been working on piracy since day one. It’s one of the things we focused on. It’s an important thing to stop in this business, so we’ve spent tonnes of money on this stuff. We just got some real important legislature done on piracy this year, these guys are bad guys.
Dana White, President & CEO of UFC, speaking at UFC Press Conference
Source: Sponsorlytix
How much revenue do illegal streamers generate?
With a cost per click (CPC) rate of $0.01 and a monthly viewership of 2,218,000, an illegal streamer could potentially generate an estimated $22,180 in ad revenue per month. This calculation assumes that the illegal streamer displays ads, and every viewer clicks on an ad each time they watch a stream.
Upon visiting a website or mobile app, users often encounter 3 to 6 ad clicks, which open in a new window before gaining access to an illegal stream. Our investigation has identified mobile apps with over 16 million downloads and websites receiving 2 to 4 million monthly visits.
It is noteworthy that advertisers on illegal streaming platforms are not obscure entities but reputable companies such as Amazon Prime, ESPN+, and Microsoft. These ads strategically target potential customers to divert them to their respective streaming platforms.
It is essential to acknowledge that these figures are estimates, and the actual revenue generated by illegal streamers may vary widely based on specific revenue-generating methods, such as subscriptions or donations, which are not factored into this calculation.
Top 20 Illegal Streaming Websites 2023
| Name | Website | Monthly Visitors |
| HesGoal | www.hesgoal.com | 2,751,670 |
| Total Sportek | www.totalsportek.com/live-kickoff/ | 2,375,000 |
| Livetv SX | http://livetv.sx/ | 2,006,750 |
| Yall Shoot | www.yalla-shoot.com/ | 1,505,000 |
| Sport Surge | https://sportsurge.net/ | 986,326 |
| NFL Bite | https://home.nflbite.com/ | 729,166 |
| Live Soccer TV | www.livesoccertv.com | 724,166 |
| VIP League | www.vipleague.lc/ | 639,168 |
| Roja directa | www.rojadirecta.me/ | 580,000 |
| Buff Streams | https://buffstreams.sx | 560,000 |
| Ronaldo7 |
www.ronaldo7.net | 557,500 |
| Yalla Shoot Today | https://goals.yalla-shoot.today | 535,000 |
| Joker Live Stream | www.jokerlivestream.net/ | 509,166 |
| Sport Stream | www.sportstream.tv/ | 500,000 |
| Football Fancast | www.footballfancast.com/vipstand | 500,000 |
| VIP Box | www.vipboxtv.se | 421,650 |
| VIP Row | www.viprow.me/ | 400,000 |
| NBA Bite | https://home.nbabite.com/ | 369,835 |
| Laola 1 |
www.laola1.at/de/ott/de-at/page/video-home | 330,830 |
| Foot Live | www.footlive.me | 322,468 |
Source: Sponsorlytix
Consuming sports has become increasing expensive, coupled with rising inflation, encourages sports fans to consume illegal streaming?
It is undeniable that sports consumption can incur significant expenses, including cable or satellite TV subscriptions, streaming service fees, and rising ticket prices. This financial burden, coupled with the increasing cost of living and inflation, poses challenges for individuals in affording legitimate sports consumption. Consequently, some sports enthusiasts may be tempted to resort to illegal streaming as a more cost-effective means of accessing content.
Read our investigation – Overpaid Footballer Salaries
For instance, to follow all English Premier League games, one would need subscriptions to Sky Sports, TNT Sports, and Amazon’s Prime Video, amounting to approximately $85 to $100 per month. Additionally, the extra cost of pay-per-view events in sports like Boxing or UFC further contributes to the financial strain. While in the UK, summer tournaments such as the FIFA World Cup or the UEFA Euros are freely accessible on BBC Sports, in most countries, viewers are compelled to pay an additional add-on fee ranging from $100 to $150 on top of their monthly subscription.
![]()
They can have as many lawyers as they want, and they can raid homes to stop fire-stick sales, but we will always find a way to stream live sports over the internet. With the way the internet works, they will never be able to fully stop internet streaming or piracy, no matter what they want to call it.
Dana White claimed last year during several press conferences that he spent millions on piracy and was trying to catch illegal streamers, but he has failed to produce a single piece of evidence for that. Why? Because it is extremely hard to track us down. There have been instances where it got close for me and a couple of my team members, but we have a fully organized structure that we follow.
We have hundreds of proxy IPs, VPNs, crawlers that scrape, thousands of domains, multiple architectures on purpose-built GPUs, and so on. The question I want to ask all the broadcasters and CEOs of all the big sports leagues is this: Is it worth spending multi-millions chasing a few “illegal streamers” and still not making any progress?
The only way they can stop us is to never live broadcast, whether through satellite or livestream over the internet. They can try to catch us if they can!
Comments from an undercover illegal streamer
Despite extended invitations for direct comments, notable figures such as Dana White, Premier League, DAZN, NCSC, beIN Sports, and others have regrettably chosen not to provide their insights, politely declining or remaining unresponsive to our email inquiries.
How big is the market? – Which countries illegally stream the most?
Source: Sponsorlytix
 The United States leads the way when it comes to illegal streaming, with 31.04% of global illegal streamers hailing from the country. This indicates a significant portion of the population engaging in this activity. Moving across the Atlantic to the United Kingdom, the figure stands at 21.37%, with over 12.6 million Brits watching sports illegally in 2023.
The United States leads the way when it comes to illegal streaming, with 31.04% of global illegal streamers hailing from the country. This indicates a significant portion of the population engaging in this activity. Moving across the Atlantic to the United Kingdom, the figure stands at 21.37%, with over 12.6 million Brits watching sports illegally in 2023.
Of that, 8.32% comes from Italy. In Italy, Serie A, the top football division, faces a severe piracy issue. League organizers warn that if fans don’t pay, media companies won’t invest in league rights, risking over a billion Euros in damage and jeopardizing 5,000 jobs. Despite 83% awareness of piracy as a crime in Italy, 38% admit to engaging in it. This trend isn’t exclusive to Italy, as one in 11 Britons confesses to watching pirate broadcasts of Premier League matches.
Canada and Germany round out the top five at 6.75% and 5.95%, respectively.
At least once a month, 53.2% of avid sports enthusiasts turn to illicit sports streaming services, with only 18% claiming they never utilize illicit sources. The probability of opting for pirated broadcasts increases with younger viewers.
How much brand value does sports sponsors lose?
Source: Sponsorlytix
When sports events are streamed illegally, sponsors actually do not miss out on the opportunity to showcase their products or services to a large audience, what they miss out on is the ability to track the effectiveness of their brands exposure or advertising campaigns. Which can make it difficult for them to measure the return on investment for their sponsorship deals.
It’s tricky to estimate the exact amount of brand value that sports sponsors lose due to illegal streaming, as it varies depending on the sponsorship deal and the specific methods that the illegal streamers are using.
Sponsorlytix studied the major sponsors of the FIFA Qatar World Cup 2022, tracking illegal visitors on streaming websites, mobile apps, and Fire Stick across more than 2000 platforms. Utilizing Sponsorlytix’s AI technology and proprietary algorithms, brand values were measured. The machine learning algorithms incorporated parameters such as logo visibility, prominence, placement, confidence score, total viewership from illegal streaming, broadcast spot prices, CPC, and other factors to determine the most accurate brand value for each sponsor.
Adidas leads the list with a brand valuation of $251.1 million, followed closely by Qatar Airways at $235.8 million. Qatar Energy secures the third position with a valuation of $219.2 million, while the Wanda Group follows closely behind at $208.9 million. Visa rounds out the top five with a valuation of $197 million.
How much revenue does TV Broadcasters lose?
Source: Sponsorlytix
When sports events are streamed illegally, broadcasters miss out on the opportunity to sell advertising and broadcasting rights to a large audience. Additionally, the illegal streaming of their content can also lead to a decrease in subscriptions and viewership, which can further impact their revenue.

Sponsorlytix estimated that the illegal streaming of sports events can cost the industry up to $1 billion annually in lost advertising and sponsorship revenues.
Last season, the Premier League blocked more than 200,000 pirate broadcasts with the financial damage estimated to cost the market around $2 million in revenue per game.
The dispute between beIN Sports and BeoutQ has been a long-standing issue, with beIN Sports accusing BeoutQ of illegally broadcasting its content in the Middle East and North Africa. The BeoutQ vs. BeIN Sports case claimed losses exceeding $1 billion.
The value of NBA and NFL broadcast rights has surged, reaching $2.7 billion and $7 billion annually, respectively. Revenue trickles down to players, team members, and league employees. However, reaching a younger audience, which consumes sports differently, poses a challenge. Cable fees, ad sales, and digital subscriptions, like ESPN+, are affected by piracy.
Pay-per-view sports suffer the most, with piracy impacting UFC’s potential loss of tens of millions annually.
Which sports are most illegally streamed?
Source: Sponsorlytix
 The global OTT (Over the Top – streaming or VOD content) content market will grow from $130 billion in 2023 to more than $180 billion in 2028. Based on Sponsorlytix data, around 39% of this total amount is categorized as “pirated,” and the phenomenon has been amplified by the lockdowns enforced during the Covid-19 pandemic
The global OTT (Over the Top – streaming or VOD content) content market will grow from $130 billion in 2023 to more than $180 billion in 2028. Based on Sponsorlytix data, around 39% of this total amount is categorized as “pirated,” and the phenomenon has been amplified by the lockdowns enforced during the Covid-19 pandemic
Football is by far the most illegally streamed sport, accounting for 27.4% of illegal downloads and views in sports. Other notable sports include basketball (just behind football at 25.5%), American Football (12.3%), MMA (8.8%) and Tennis (6.2%). Other sporting events such as boxing, athletics championships, motor sports etc make up the top 10.
The trend is not going anywhere despite the efforts from the UFC or Premier League. There are more than 51 million people a month worldwide who visit pirate broadcast sites.
How to fix the issue of illegal sports streaming? Can sports governing bodies and broadcasters work with them in any capacity?
The anti-piracy authorities engage in a multi-faceted battle, focusing on domain names, the individuals orchestrating them, their servers, or the origin of the streams. They utilize bots and socially adept staff to track down streams that infringe on copyrights.
Employing technologies such as fingerprinting or watermarking, which involves overlaying a unique, imperceptible layer on each feed, they can pinpoint the original copy of the stream and disrupt it. However, the pirates often manage to stay a step ahead by preparing backups and covering their tracks. Despite leagues sending takedown notices, these are frequently ignored. Server blocking is effective only on a country-by-country basis where laws permit, and domain-blocking loses efficacy when criminals switch from “.com” to “.us” or “.live” domains to continue their operations.
each feed, they can pinpoint the original copy of the stream and disrupt it. However, the pirates often manage to stay a step ahead by preparing backups and covering their tracks. Despite leagues sending takedown notices, these are frequently ignored. Server blocking is effective only on a country-by-country basis where laws permit, and domain-blocking loses efficacy when criminals switch from “.com” to “.us” or “.live” domains to continue their operations.
Leagues and broadcasters are working to enhance their response to illegal streaming. In May 2021, the European Parliament urged Member States to implement legal measures supporting crackdown efforts. European legislators adopted a proposal to combat online piracy of live sporting events, including the option to block illegal broadcasts within 30 minutes. They emphasized that the new rules should not target unaware consumers but should confront the issue at its source. Additionally, they called on the European Commission to amend legislation on intellectual property rights concerning live sporting events, which currently lack protection under the bloc’s copyright rules.
Top 20 Illegal Streaming Mobile Apps (2023)
| Name | Appstore Link | Downloads |
| Live Cricket TV HD | https://tinyurl.com/54bx8jch | 16,000,000+ |
| Live Football TV Euro | https://tinyurl.com/4ujr2pmc | 10,000,000+ |
| Live Football on TV | https://tinyurl.com/45r46n5a | 2,000,000+ |
| Live Cricket TV Matches 2023 | https://tinyurl.com/bde4n7pu | 2,000,000+ |
| Live Sports HD TV | https://tinyurl.com/yb8a36kx | 2,000,000+ |
| Live Sports TV Listings Guide | https://tinyurl.com/yb83mj2k | 2,000,000+ |
| Soccer Live on TV |
https://tinyurl.com/y3822yju | 2,000,000+ |
| Sport.pl LIVE | https://tinyurl.com/98n2jt35 | 2,000,000+ |
| Dofu Livestream | https://tinyurl.com/m595h2ru | 2,000,000+ |
| Foot Live Sat – TV Channels | https://tinyurl.com/mtw3ac3t | 1,000,000+ |
| India – Live IPTV Channels | https://tinyurl.com/4sd88p28 | 1,000,000+ |
| ND vs SA Cricket Live Match | https://tinyurl.com/w3yyxxwv | 1,000,000+ |
| sporttotal.tv – Live Sport | https://tinyurl.com/46xxukay | 200,000+ |
| SportEventz – Live sport on TV | https://tinyurl.com/3eb38ry5 | 200,000+ |
| Direct Sports Network | https://tinyurl.com/yz23pewy | 200,000+ |
| Live Streaming NFL NCAAF NBA | https://tinyurl.com/mr3769yy | 200,000+ |
| My Sport Live | https://tinyurl.com/3rmmf675 | 200,000+ |
| Live Footbal TV Sports HD | https://tinyurl.com/yc4kebab | 200,000+ |
| USA – Live TV (Entertainment) | https://tinyurl.com/mr3tpc77 | 200,000+ |
| Live TV | https://tinyurl.com/mt3wn4p7 | 200,000+ |
Source: Sponsorlytix
Leagues and broadcasters are working to enhance their efforts in combating illegal streaming. In May 2021, the European Parliament called on Member States to implement legal measures to bolster crackdown initiatives. European lawmakers approved a proposal to address online piracy of live sporting events, incorporating the option to swiftly block illegal broadcasts within a 30-minute timeframe. MEPs said the new rules should not target consumers, who are often not aware that the content they are watching is illegal, but insure the issue is confronted at source.
Additionally, they called on the European Commission to amend the legislation on intellectual property rights in regard to live sporting events, which are not protected by the bloc’s copyright rules.
Legal measures to combat illegal streaming often lag behind technological advancements, making it challenging to curb the proliferation of such platforms effectively. The issue raises critical questions about the future of intellectual property protection in the digital age. Content creators, distributors, and legal authorities must collaborate to devise innovative strategies that keep pace with the evolving landscape of digital piracy.
While the legal landscape regarding illegal streaming investigations is intricate, the lack of a unified approach across jurisdictions further complicates matters. Piracy knows no borders, and a global effort is essential to effectively tackle this menace. The collaboration between content creators, law enforcement agencies, and international organizations becomes imperative to formulate and implement comprehensive solutions.



















